Is A Torn Lisfranc Ligament Surgically Repaired
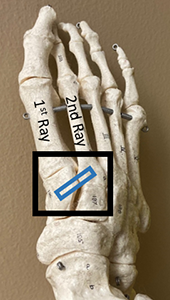
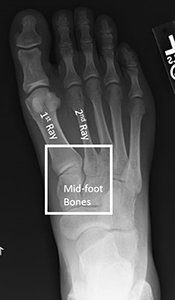
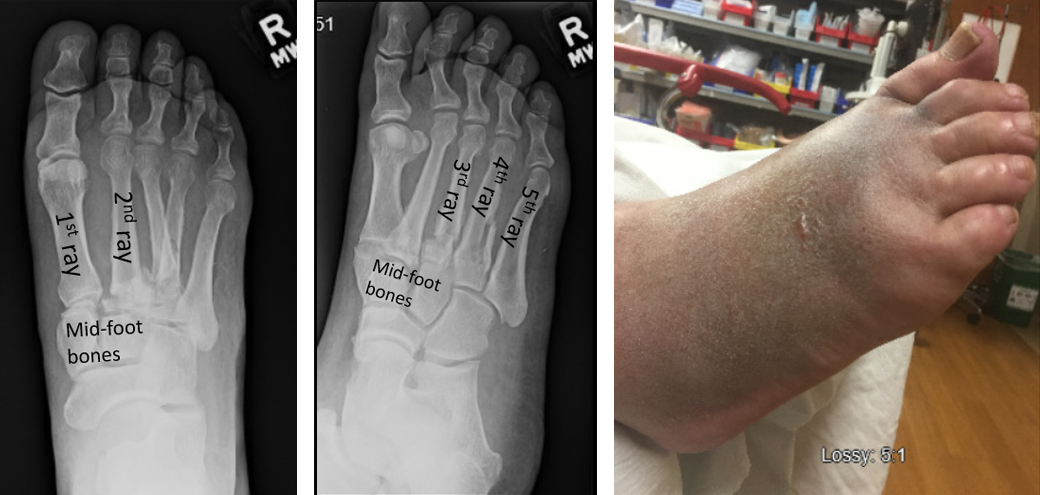
Basic Anatomy
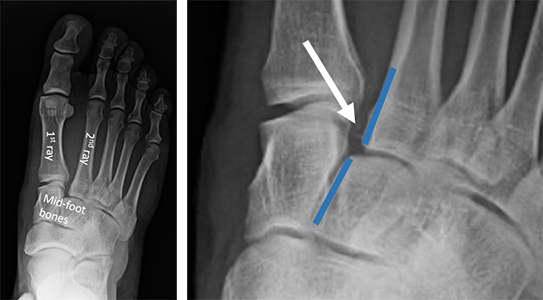
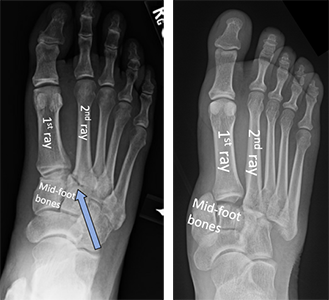
A "LisFranc" injury is an injury to the joint betwixt the long bones in the foot (metatarsals) and the basic they connect to (tarsal bones). This injury can affect the ligaments (soft tissue that connects bone to bone) of these basic and/or include fractures of the bones themselves. The injury tin can hurt the whole foot or be limited to part of the human foot.
Since there is very petty peel over the basic of the human foot, nerves and arteries that lie directly on tiptop of the basic can be injured too. This injury can cause the pes to swell a peachy deal. The bones tin can push on the pare causing damage or blistering of the skin.
The bones and ligaments are important for keeping the shape of your human foot. When you step down, your basic and ligaments resist that force and go on the bones in their proper places, maintaining the arch of your foot. When your ligaments or bones are injured, your pes can collapse, which causes pain while walking.
Machinery and Epidemiology
LisFranc injuries are rare and account for less than 1 percentage of all fractures. They happen after trauma to a pes from a fall, motor vehicle accident, a crush injury, or even an athletic injury. This can happen when you have placed your weight on your human foot, with your toes pointed down and yous twist your foot. Since this injury can happen with injuries to the ligaments only or the bones and ligaments, information technology can happen in many different ways. A crush injury that causes a LisFranc injury can look very different from an athletic injury.
Initial Treatment
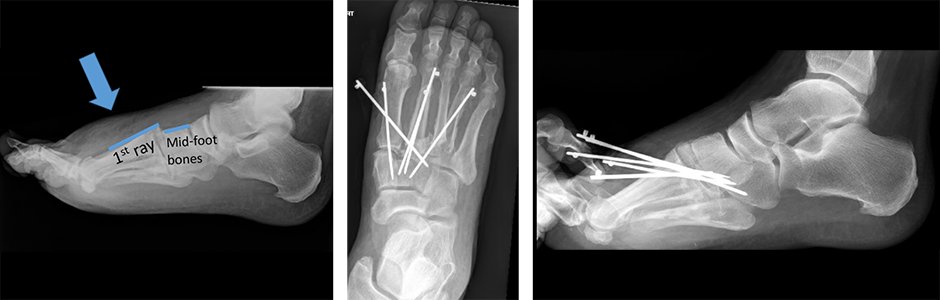
These injuries will make the heart of your foot injure when yous try to walk or stand up. Your foot can swell upwardly. The pain may exist and then bad yous tin can't walk. A doctor volition examine your foot to make sure your skin is okay and that the bones are non pushing on information technology. Ten-rays of your foot will be taken, and x-rays of your other, uninjured human foot may as well exist taken for comparison. A CT scan may also be done, because information technology can be hard to run across the details of your injury using just ten-rays. This is specially true if just the ligaments are injured.
If your bones are pushing confronting the skin or are far away from where they should exist, your doctor may attempt a reduction (pushing the bones back into place). This can exist done in the emergency room or the operating room. If the basic came through the skin or they can't be put back into place, you volition normally have to go to the operating room.
A splint or a boot may be used to protect your foot and to help with your hurting by stabilizing your injury. More often than not, your doc won't want yous putting any weight onto your human foot, and you should drag your pes to help reduce swelling. Every bit long as your peel is okay and your bones are in a expert position, you tin usually go domicile from the emergency room and be seen by an orthopaedic surgeon in a clinic on some other day.
Full general Treatment
LisFranc injuries often require surgery. There are times when the bones are lined up in a way that allows them to heal without surgery. In that setting, they more often than not crave a cast or splint and no weight bearing for several weeks to months.
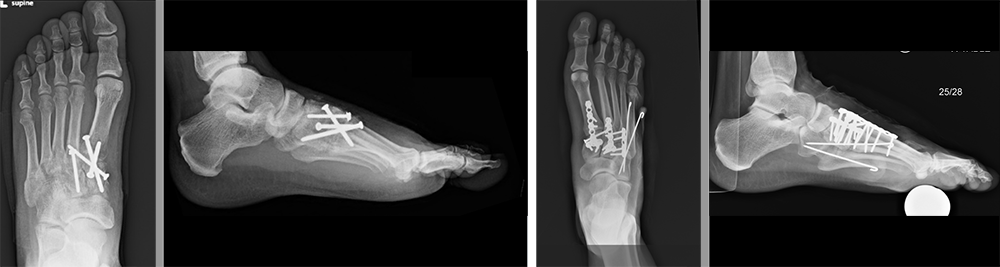
Surgery can exist done several means. Screws, plates and screws or even pins can exist used to hold your basic together. Your surgeon volition brand the decision how best to fix your specific injury. The bones can be fixed in a way that allows the ligament or bones to heal. This may keep the joints between the basic as they were. Your surgeon may too decide to fuse the bones together past removing the cartilage between the basic. A discussion nigh the risks and benefits of both of these options should exist had with your surgeon. In surgery, pins may be placed through the pare to hold the bones in place. These may exist taken out in clinic a few weeks afterwards. This can be slightly painful, but in general is very quick and many patients tolerate the pain well.
If the bones are fixed and not fused together, the plates, screws or pins may need to exist taken out later. This commonly means another surgery that requires anesthesia.
Postoperative Care
Later surgery, information technology is important to elevate your human foot to reduce swelling. The pare on the top of your foot is sparse, and swelling causes tension on the wound. Usually, you volition be in a splint, cast or a kicking for several weeks to months. This protects the bones and ligaments while they are healing. You volition besides probably not be able to put weight on your foot for two-3 months while it is healing. This volition require using crutches, a walker, a knee scooter, or even a wheelchair to get around safely. The nigh important thing is to follow the instructions of your surgeon. Falls, putting weight on your foot also early, or too much swelling tin can cause problems that may bear upon how y'all heal.
Later a period of not putting weight on your foot, you may first concrete therapy. The therapist may work on movement of your talocrural joint, and once canonical by your surgeon they may work with you on putting some weight on your pes. It is by and large several months before you can put your full weight on your foot. While this may exist frustratingly slow, it is of import for proper healing of your bones and ligaments. It is important to follow the instructions of your surgeon.
Long Term
LisFranc injuries can have long term effects on your foot. Some people are able to get dorsum to the activity level they had before the injury. All the same, it is common to have some persistent hurting, stiffness, and weakness. This can happen even after a surgery and healing period that goes perfectly. Your foot takes all the weight of your body with each step. There is a lot of stress across these small bones and ligaments, and after a LisFranc injury they may not exist as skilful every bit they were before your injury. This may mean that you have to change your activities. It may also hateful using special shoes or braces. Sometimes people require more surgery in the future.
More Information
- American University of Orthopaedic Surgeons
---
Christopher Domes, MD
Edited by the OTA Patient Education Committee and David Sanders, MD (section atomic number 82)
All ten-rays and pictures taken from the personal drove of Dr. Domes
Source: https://ota.org/for-patients/find-info-body-part/3721
Posted by: aguirresplight.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is A Torn Lisfranc Ligament Surgically Repaired"
Post a Comment